-
Research Article
-
Uniform Elongation of Steel Reinforcing Bars manufactured to Korean Standards
한국 표준에 따라 생산된 철근의 균일연신율
-
Eun-Ho Lee, Se-Rim Pyo, Hyeon-Woo Lee, Tae-Won Oh, Jae-Hoon Lee
이은호, 표세림, 이현우, 오태원, 이재훈
- Tensile tests were conducted on 149 reinforcing bar specimens manufactured in Korea in accordance with KS D 3504. The test results were …
한국의 철근표준 KS D 3504에 따라 한국에서 생산된 철근을 대상으로 인장시험을 실시하여 총 149개의 균일연신율 실측값을 얻었고, 강종에 따른 경향을 분석하였으며 Eurocode …
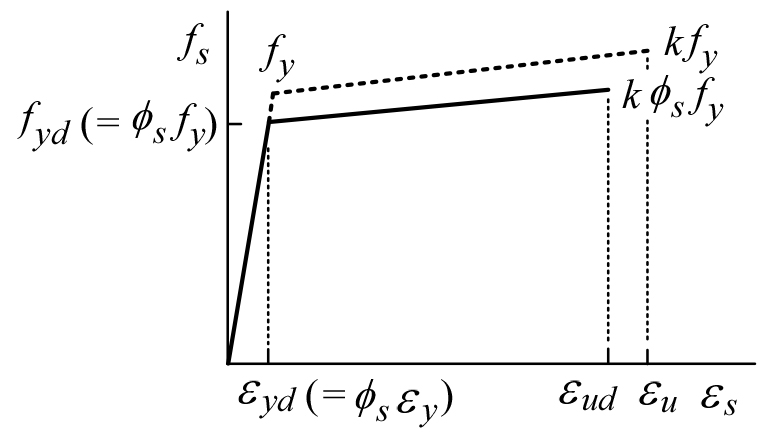
- Tensile tests were conducted on 149 reinforcing bar specimens manufactured in Korea in accordance with KS D 3504. The test results were analyzed with respect to steel grades and compared with the minimum requirements of Eurocode 2 and ACI 318-19 Code. Specimen diameters ranged from 9.53 mm (D10) to 57.3 mm (D57), with yield strengths of 426–816 MPa and tensile strengths of 571–962 MPa. It was found that uniform elongation tends to decrease as yield and tensile strength increase. For general-purpose reinforcing bars with specified yield strengths of 600 MPa or less, all specimens showed uniform elongations greater than 5 %, thus satisfying Eurocode 2. All SD400S seismic bars exhibited greater than 10 % uniform elongations, meeting both Eurocode 2 (7.5 %) and ACI 318-19 Code (9 % for Grade 420 MPa steel). However, 4 of 10 SD500S and 7 of 13 SD600S specimens fell below 7.5 %, failing to satisfy Eurocode 2, and 3 of 10 SD500S and 4 of 13 SD600S specimens did not meet the ACI 318-19 Code minimum requirement of 7 % for Grade 550 MPa steel. Based on these results, revision proposals for KS D 3504 and the Korean Concrete Bridge Design Code(Limit State Design Method) were suggested.
- COLLAPSE
한국의 철근표준 KS D 3504에 따라 한국에서 생산된 철근을 대상으로 인장시험을 실시하여 총 149개의 균일연신율 실측값을 얻었고, 강종에 따른 경향을 분석하였으며 Eurocode 2와 ACI 318-19 Code의 최소 균일연신율 조건과 비교하였다. 시험편의 지름은 9.53 mm (D10)에서 57.3 mm (D57)까지의 범위로, 인장시험 결과 항복강도는 426~816 MPa의 범위를 보였으며 인장강도는 571~962 MPa의 범위를 보였다. 측정된 균일연신율 값은 철근의 항복강도와 인장강도가 증가할수록 감소하는 경향을 보였다. 설계기준항복강도가 600 MPa 이하로 건설현장에서 사용되고 있는 일반구조용 철근은 모두 5 %를 초과하는 균일연신율로 Eurocode 2의 최소 균일연신율 조건을 만족하였다. 내진용 SD400S 철근 시험편은 10개 모두 10 %를 초과하는 균일연신율로 Eurocode 2의 최소 균일연신율 조건인 7.5 %를 만족하였고, 설계기준항복강도 420 MPa에 대한 ACI 318-19 Code의 최소 조건 9 % 또한 만족하였다. 그러나 내진용 SD500S 철근 시험편은 10개 중 4개, SD600S 철근 시험편은 13개 중 7개가 7.5 % 미만으로 Eurocode 2의 최소 균일연신율 조건을 만족하지 못하였다. 또 SD500S 철근 시험편 10개 중 3개, SD600S 철근 시험편은 13개 중 4개가 설계기준항복강도 550 MPa에 대한 ACI 318-19 Code의 최소 조건 7 %를 만족하지 못하였다. 이 결과를 바탕으로 KS D 3504와 한국 콘크리트교 설계기준(한계상태설계법)의 개정안을 제안하였다.
-
Uniform Elongation of Steel Reinforcing Bars manufactured to Korean Standards
-
Research Article
-
UHPC Bond Strength Prediction in Precast Joints Using Machine Learning
머신러닝 기법을 활용한 프리캐스트 연결부 UHPC 부착강도 예측
-
Dong Kyu Lim, Ho Bi Kang, Young Jin Kim, Myoung Sung Choi
임동규, 강호비, 김영진, 최명성
- This study experimentally investigated the bond performance of precast bridge-deck joints using ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) to enhance structural efficiency and constructability. Conventional …
본 연구는 프리캐스트 교량 바닥판 연결부에 초고성능 콘크리트(UHPC)를 적용하여 부착성능을 평가하고, 시공성과 구조적 효율을 향상시키는 것을 목적으로 한다. 기존 루프 이음 방식은 …
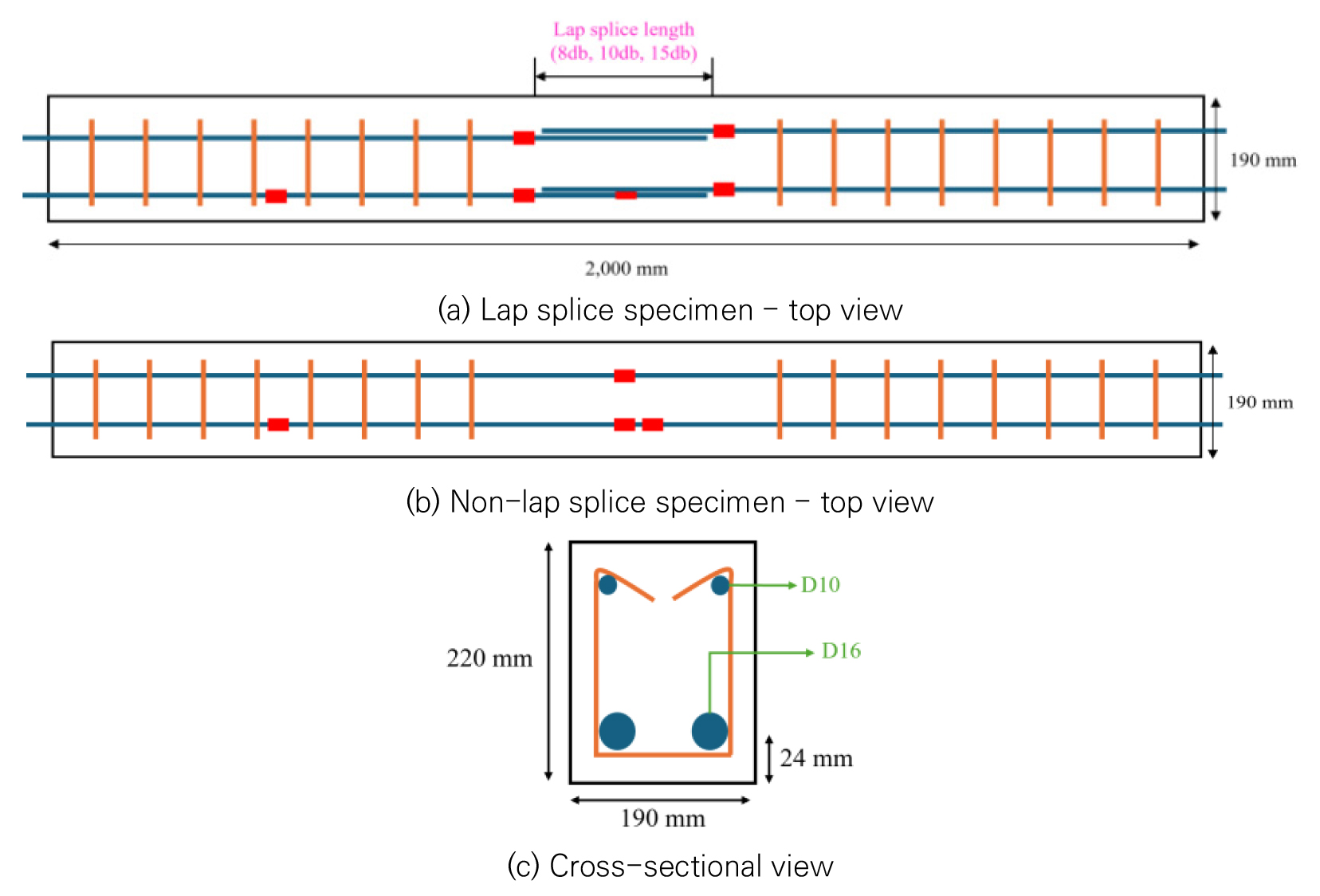
- This study experimentally investigated the bond performance of precast bridge-deck joints using ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) to enhance structural efficiency and constructability. Conventional loop-splice joint details often require long splice lengths and may reduce construction productivity. UHPC was examined as a filling material to secure adequate structural performance while shortening the splice length. Fourteen splice specimens were fabricated with varying compressive strengths (80, 100, and 120 MPa) and splice lengths (8d_b, 10d_b, and 15d_b), and splice tests were conducted under four-point loading. The test results demonstrated that UHPC, due to its high compressive strength and fiber reinforcement, provided sufficient load transfer and crack control even at short splice lengths. However, existing design provisions such as Eurocode 2, the Korean Highway Bridge Design Code, ACI 318, and the Structural Design Guideline for Fiber-Reinforced SUPER Concrete were found to be limited in reflecting the distinct bond characteristics of UHPC. To address this, machine learning techniques were employed to develop data-driven bond strength and development-length prediction models. Random forest and SHAP analysis were used to identify influential parameters, and symbolic regression (PySR) was applied to derive interpretable equations. The proposed models showed high prediction accuracy and are expected to improve the design reliability and efficiency of precast UHPC joint systems.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 프리캐스트 교량 바닥판 연결부에 초고성능 콘크리트(UHPC)를 적용하여 부착성능을 평가하고, 시공성과 구조적 효율을 향상시키는 것을 목적으로 한다. 기존 루프 이음 방식은 긴 이음길이를 요구하여 시공성과 구조 효율성이 저하되는 한계가 있다. 이에 UHPC를 충전재로 활용하여 이음길이를 단축하면서도 충분한 구조 성능 확보 가능성을 검토하였다. 압축강도(80, 100, 120 MPa)와 이음길이(8d_b, 10d_b, 15d_b)를 변수로 한 총 14개의 실험체를 제작하고, 4점 재하 실험을 수행하였다. 실험 결과, UHPC는 높은 압축강도와 섬유보강 효과로 인해 짧은 이음길이에서도 우수한 하중전달성능과 균열제어 능력을 확보할 수 있음을 확인하였다. 반면 Eurocode 2, 한국 도로교 설계기준, ACI 318 및 섬유보강 SUPER 콘크리트 설계지침 등 기존 기준은 UHPC의 특수한 부착거동을 충분히 반영하지 못하는 한계가 나타났다. 이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해 머신러닝 기반의 데이터 분석을 수행하였으며, 변수 영향도 분석(Random Forest 및 SHAP)과 상징회귀(PySR)를 통해 부착강도 및 정착길이 예측식을 제안하였다. 제안된 모델은 높은 예측 정확도를 보였으며, 프리캐스트 UHPC 연결부 설계의 신뢰성 향상과 효율적인 시공 계획 수립에 기여할 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
UHPC Bond Strength Prediction in Precast Joints Using Machine Learning
-
Research Article
-
A Review of International Design Guidelines and Deterioration Range Estimation for Concrete Repairs
콘크리트 구조물 보수공사의 해외 기준 및 열화범위 산정 연구 고찰
-
Seyoon Yoon, Yoseok Jeong, Min Kyoung Kim, Geunhyeong Min, Jinwoong Choi, WooSeok Kim
윤세윤, 정유석, 김민경, 민근형, 최진웅, 김우석
- While the importance of maintenance increases with the aging of concrete structures, premature re-deterioration after repair remains a persistent problem. This is …
콘크리트 구조물의 노후화가 진행됨에 따라 유지관리의 중요성이 커지고 있으나, 보수 후 조기 재열화 문제가 지속적으로 발생하고 있다. 이는 주로 염화물 등 열화 …
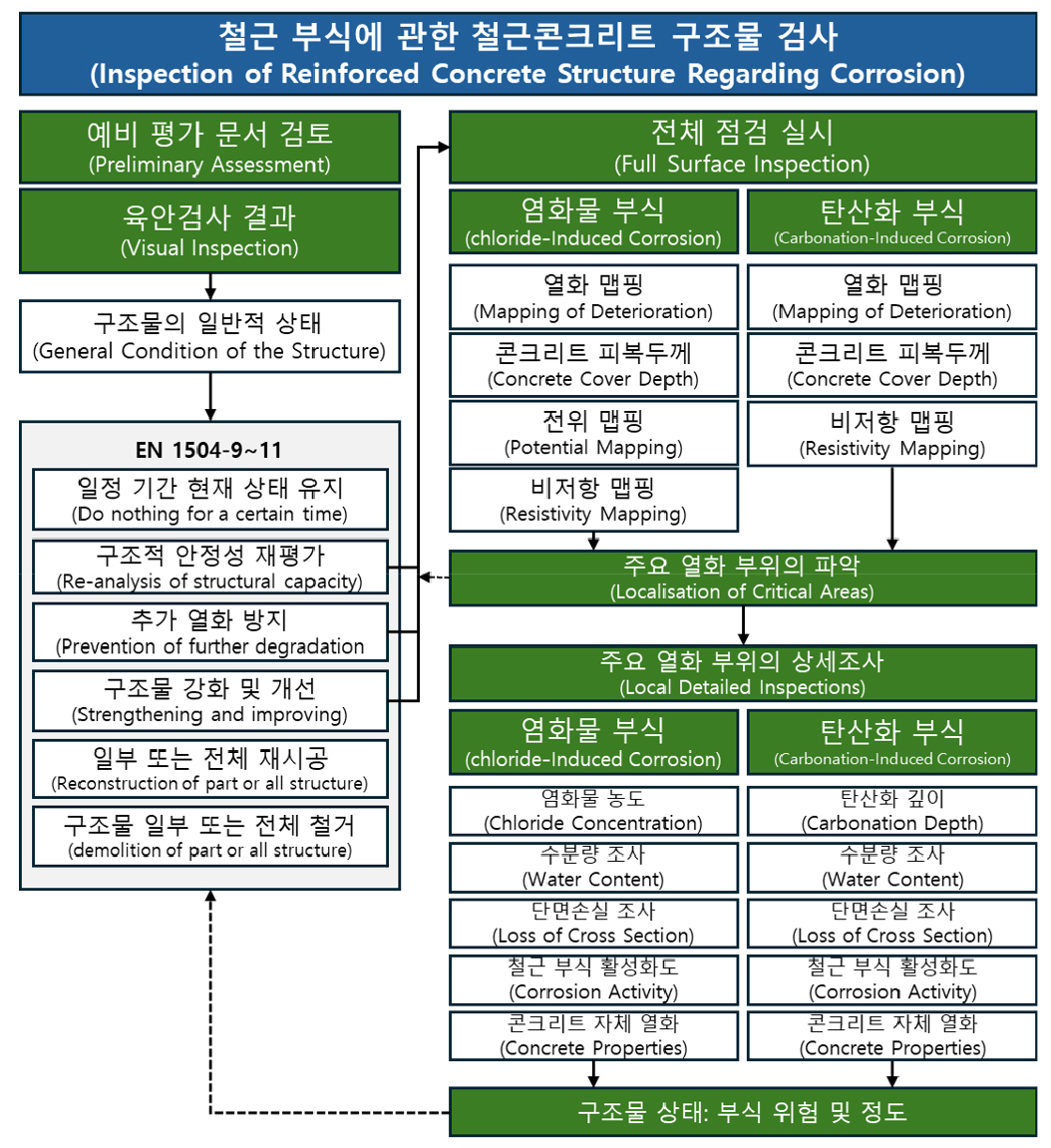
- While the importance of maintenance increases with the aging of concrete structures, premature re-deterioration after repair remains a persistent problem. This is primarily due to incomplete removal of deterioration causes, such as chlorides, during the repair process. This study aims to secure the long-term performance of concrete structures by reviewing international repair guidelines (EN 1504, ACI 546R-14) and recent research trends in deterioration range estimation. International guidelines emphasize accurate estimation of the deterioration range, including potential deterioration areas, through systematic condition assessment, and recommend the use of non-destructive testing (NDT) techniques such as potential mapping. Furthermore, this study analyzes rational repair range setting methods and optimal repair strategies through empirical field studies and probabilistic prediction model research. The results confirm that complete removal of deteriorated areas and thorough surface preparation are key factors for successful repair, and suggest that preventive repair strategies can be economical and effective from a long-term perspective. This study is expected to serve as fundamental data for improving the quality and securing the long-term performance of concrete repair works in Korea.
- COLLAPSE
콘크리트 구조물의 노후화가 진행됨에 따라 유지관리의 중요성이 커지고 있으나, 보수 후 조기 재열화 문제가 지속적으로 발생하고 있다. 이는 주로 염화물 등 열화 원인이 완전히 제거되지 않은 채 보수가 이루어지기 때문이다. 본 연구는 콘크리트 구조물의 장기공용성 확보를 위해 국제 보수 지침(EN 1504, ACI 546R-14)과 열화범위 산정 관련 최신 연구 동향을 고찰하였다. 국제 지침들은 체계적인 상태 평가를 통해 잠재적 열화 영역까지 포함하는 정확한 열화범위 산정을 강조하고 있으며, 이를 위해 전위 매핑 등 비파괴 검사 기법의 활용을 권장한다. 또한, 현장 실증 연구와 확률론적 예측 모델 연구를 통해 합리적인 보수 범위 설정 방안과 최적의 보수 전략을 분석하였다. 연구 결과, 열화부의 완전한 제거와 철저한 바탕면 처리가 보수 성공의 핵심 요인임을 확인하였으며, 장기적인 관점에서 예방적 보수 전략이 경제적이고 효과적일 수 있음을 시사한다. 본 연구는 국내 콘크리트 보수 공사의 품질 향상과 장기공용성 확보를 위한 기초 자료로 활용될 수 있을 것이다.
-
A Review of International Design Guidelines and Deterioration Range Estimation for Concrete Repairs
-
Research Article

-
Electromechanical Behavior of Textile Reinforced Cementitious Composites Under Uniaxial Load
일축 하중 하의 직조물 보강 시멘트 복합재료의 전기역학적 거동
-
Jun Sik Cho, Tae Uk Kim, Dong Joo Kim
조준식, 김태욱, 김동주
- In this study, the electromechanical behavior of textile reinforced cementitious composites (TRCCs) reinforced by carbon and glass textiles (CT and GT) under …
본 연구에서는 노후 콘크리트 구조물에 대한 효율적인 보강 및 건전성 모니터링 기술 개발을 목적으로, 카본(carbon textile, CT) 및 유리 섬유 직조물(glass textile, …
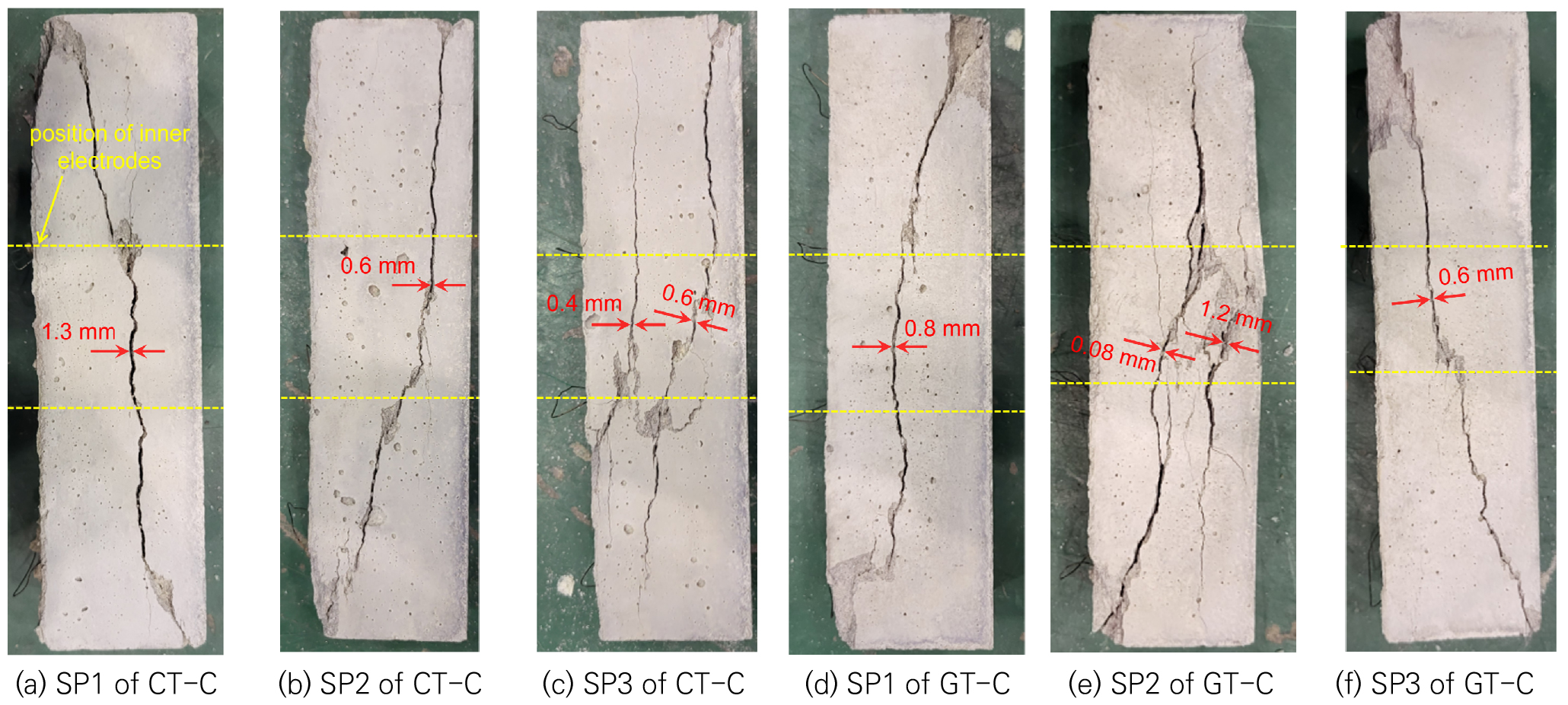
- In this study, the electromechanical behavior of textile reinforced cementitious composites (TRCCs) reinforced by carbon and glass textiles (CT and GT) under uniaxial tension and compression was investigated using DC multimeter, aiming to develop an efficient strengthening and structural health monitoring technology for deteriorated concrete structures. Under tension, the fractional change in electrical resistivity (FCR) of the tensile specimens reinforced by CT (CT-T) varied significantly, ranging from –3.35 % to –94.47 % at the first-cracking point, and from –57.1 % to 15.33 % at the post-cracking point. These variations are attributed to the discontinuous changes in conductive pathways caused by the combined effects of telescopic pullout of carbon filaments, interfacial shear slip, and bridging effect of the textile as the tensile strain increased. Under compression, the FCR of CT specimens (CT-C) at failure (93.53 % to 475.00 %) also exhibited highly irregular behavior due to unstable fluctuations in the conductive network, resulting from local buckling and shear deformation of the filaments within the textile. In contrast, the specimens reinforced by GT (GT-T) showed a sharp increase in electrical resistivity only at failure under tension, as the glass textile had little influence on the conductive network within the matrix. In all cases, the electromechanical behavior of the specimens showed relatively consistent trends in response to external loading. The experimental results confirmed that the electromechanical behavior of TRCCs is significantly influenced by the electrical conductivity and interfacial behavior of the embedded textile, and that CTs are suitable for use as self-sensing materials. Moreover, further analysis of the electromechanical behavior of TRCCs is expected to enable identification of textile–matrix failure modes under external loading conditions.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 노후 콘크리트 구조물에 대한 효율적인 보강 및 건전성 모니터링 기술 개발을 목적으로, 카본(carbon textile, CT) 및 유리 섬유 직조물(glass textile, GT)이 보강된 직조물 보강 시멘트 복합재료(textile reinforced cementitious composites, TRCCs)의 일축 인장 및 압축 하중에 따른 전기역학적 거동을 조사하였다. 인장 하중 하에서 카본 섬유 직조물이 보강된 인장 시험체(CT-T)의 초기 및 최종 균열 시점 전기저항 변화율(fractional change in electrical resistivity, FCR)은 각각 –3.35%~–94.47% 그리고 –57.1%~15.33%로 편차가 크게 발생하였는데, 이는 인장 하중이 증가에 따라 카본 섬유 직조물 내 필라멘트들의 단계적 인발(telescopic pullout), 전단 인발(shear slip), 직조물의 가교 작용 등에 복합적으로 영향을 받으면서 전도성 경로가 불연속적으로 변형되었기 때문이다. 압축 하중 하에서도 CT의 파단 시점 FCR(93.53%~475.00%)은 직조물 내 필라멘트의 국부 좌굴 및 전단변형에 따른 전도성 네트워크가 불규칙한 변동으로 매우 불규칙한 거동을 나타냈다. 반면, 유리 섬유 직조물을 보강한 시험체(GT-T)는 유리 섬유 직조물이 매트릭스 내부 전도성 경로에 미치는 영향이 적어 인장 하중에 의해 파단될 때의 전기저항률 급증 거동만이 확인되었다. TRCCs의 전기역학적 거동은 보강된 직조물의 전기전도도 및 계면 거동에 따라 크게 변화하는 것이 실험을 통하여 확인되었으며 CT가 자가센싱 용도로 사용에 적합하였다. 추후 TRCCs의 전기역학적 거동 분석을 통하여 외부 하중 하에서 직조물-매트릭스 파괴 모드를 구분 가능할 것으로 기대된다.
-
Electromechanical Behavior of Textile Reinforced Cementitious Composites Under Uniaxial Load
-
Research Article
-
A Study on the Field Applicability of the Wire-based Robot Position Control System for Under-bridge Inspection
교량 하면 점검용 와이어 기반 로봇 위치 제어 시스템 현장 적용성 검토
-
Namgyu Kim, Young-soo Park, Hyunjin Lee, Sang-Yoon Lee
김남규, 박영수, 이현진, 이상윤
- The wire-based under-bridge inspection technique is a method that utilizes multiple wires to bring a lateral truss close to the bridge underside, …
와이어 기반 교량 하면 점검 기술은 복수의 와이어를 이용하여 횡방향 트러스를 교량 하면에 접근시키고, 교축 방향으로 이동시키며, 횡방향 트러스 상부에 설치된 영상 …
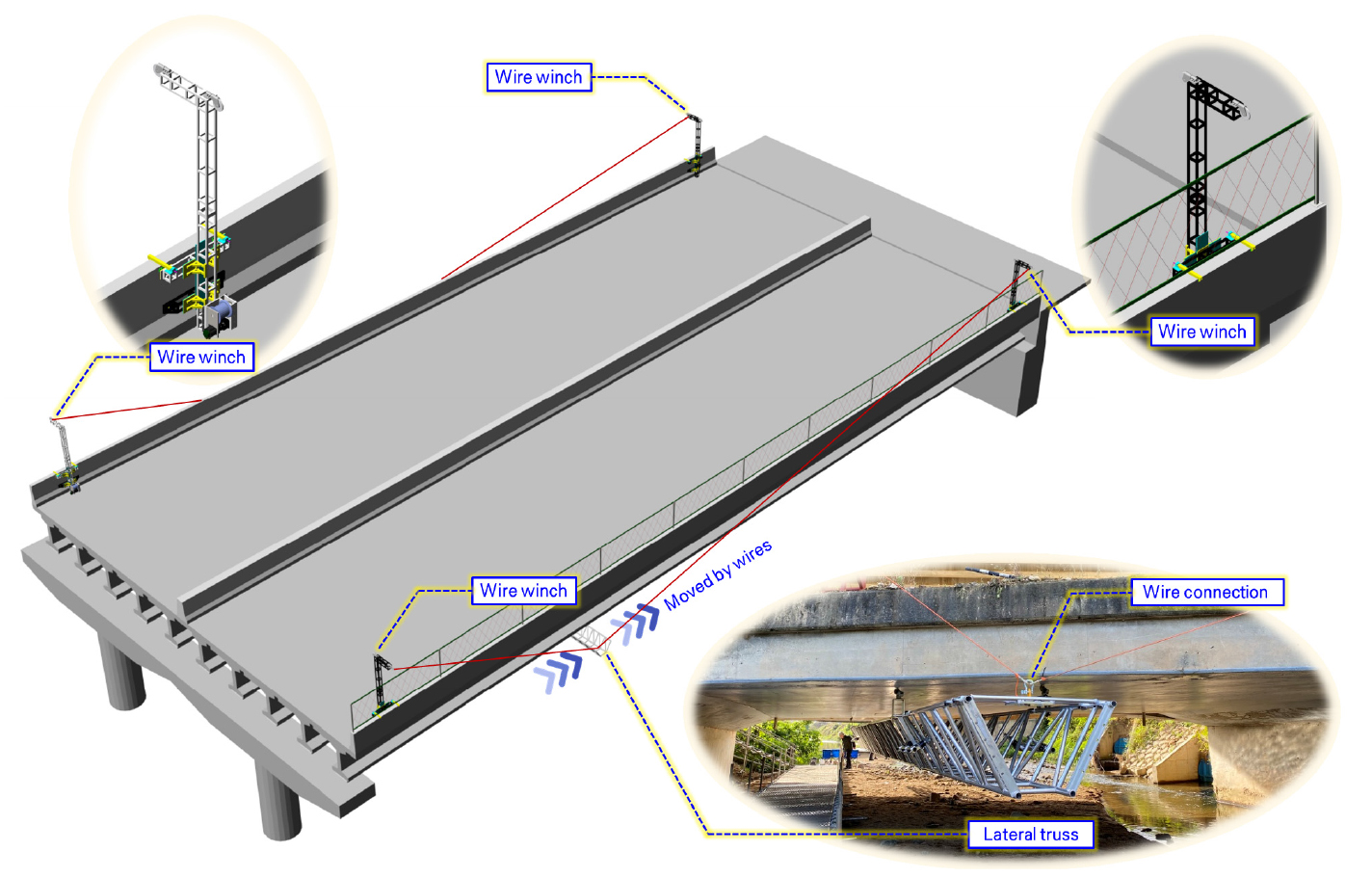
- The wire-based under-bridge inspection technique is a method that utilizes multiple wires to bring a lateral truss close to the bridge underside, move it in the longitudinal direction of the bridge, and automatically collect images of the bridge underside using a Robo-cam installed on the upper part of the lateral truss. In this study, for the integration and functional improvement of the wire-based robot position control system, we proposed improvements to existing components and new sub-components with added functionalities, fabricated these components, and applied the overall system to an actual bridge to evaluate its field applicability. The results of the field application confirmed that the lateral truss, positioned on the bridge’s underside, could be operated with a high control precision of up to approximately 6 mm using the wire winches installed on the bridge deck. However, for this system to be deployed for actual bridge inspection, the development of components for winch installation and integrated testing with the Robo-cam system are necessary.
- COLLAPSE
와이어 기반 교량 하면 점검 기술은 복수의 와이어를 이용하여 횡방향 트러스를 교량 하면에 접근시키고, 교축 방향으로 이동시키며, 횡방향 트러스 상부에 설치된 영상 수집 로봇(로보캠)을 통해 양질의 교량 하면 영상을 자동으로 수집하는 방법이다. 본 연구에서는 시스템의 통합과 기능 개선을 위하여 기존 부재에 대한 개선안과 새로운 기능이 부여된 부부재를 제안하고, 이들 부재를 제작하였으며, 전체 시스템을 실제 교량에 적용하여 현장 적용성을 판단하였다. 현장 적용 결과, 교량 상부에 설치된 와이어 윈치를 이용하여 교량 하면에 위치한 횡방향 트러스를 최대 약 6 mm의 높은 제어 정밀도를 갖고 운용할 수 있음을 확인하였다. 단, 본 시스템을 실제 교량 점검에 투입하기 위해서는 윈치 설치용 부재의 개발 및 로보캠 시스템과의 통합 테스트가 필요하다.
-
A Study on the Field Applicability of the Wire-based Robot Position Control System for Under-bridge Inspection
-
Research Article
-
Data Augmentation and Interpretable Deep Learning for Remaining Life Prediction of Highway Bridges
고속도로 교량 결함도지수의 장기 예측을 위한 데이터 증강 및 Deep Lattice Network 모델 개발
-
Chaemin Lee, Yangrok Choi, Jung Sik Kong
이채민, 최양록, 공정식
- Machine learning models are commonly used for long-term prediction of bridge deterioration. However, tree-based models such as XGBoost exhibit fundamental extrapolation limitations, …
교량 열화의 장기 예측에는 기계학습 모델이 널리 사용된다. 그러나 XGBoost와 같은 트리 기반 모델은 학습 데이터 범위를 벗어나면 예측값이 일정 수준에서 수렴하여 …
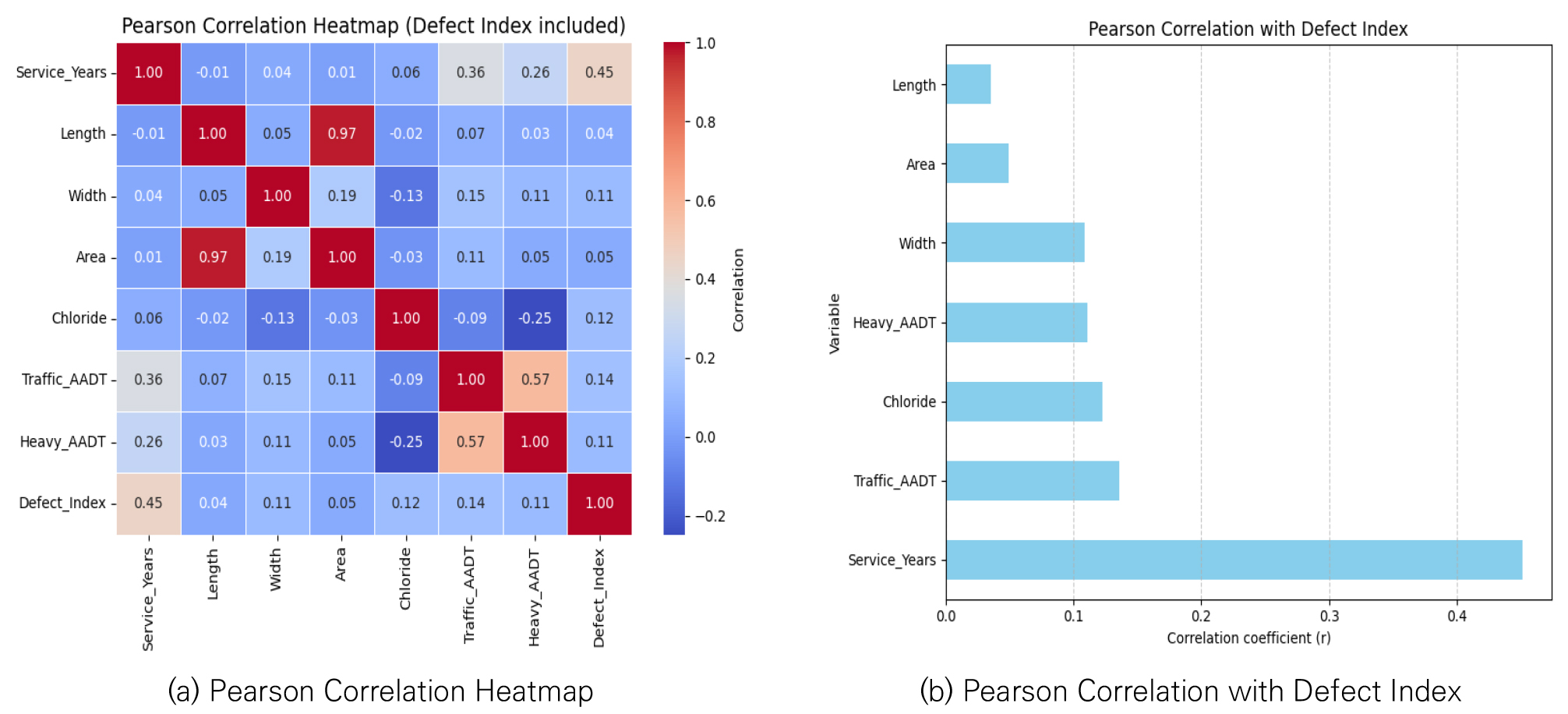
- Machine learning models are commonly used for long-term prediction of bridge deterioration. However, tree-based models such as XGBoost exhibit fundamental extrapolation limitations, where predictions converge to constant values beyond the training data range, failing to capture continued deterioration. This study develops a Deep Lattice Network (DLN) model with monotonicity constraints to overcome this limitation. Monotonicity constraints were applied to key variables including service years, chloride, and traffic volume to ensure physically valid predictions in extrapolation regions. To address the scarcity of high-defect data, balanced data augmentation was implemented to expand the training dataset. The DLN model successfully predicted that the vast majority of bridges would reach D-grade, while XGBoost predicted only a negligible fraction due to prediction saturation. Data augmentation significantly improved prediction performance by reducing prediction errors and substantially increasing the number of test samples in the rare high-defect region. The results demonstrate that combining monotonicity constraints with balanced data augmentation effectively resolves both extrapolation and imbalanced data problems in bridge deterioration prediction, demonstrating the potential for realistic long-term maintenance planning.
- COLLAPSE
교량 열화의 장기 예측에는 기계학습 모델이 널리 사용된다. 그러나 XGBoost와 같은 트리 기반 모델은 학습 데이터 범위를 벗어나면 예측값이 일정 수준에서 수렴하여 지속적인 열화를 포착하지 못하는 근본적인 외삽 한계를 보인다. 본 연구에서는 이러한 한계를 극복하기 위해 단조성 제약을 적용한 Deep Lattice Network(DLN) 모델을 개발하였다. 공용년수, 염화물, 교통량 등 주요 변수에 단조성 제약을 적용하여 외삽 구간에서도 물리적으로 타당한 예측을 보장하였다. 고결함도 데이터의 희소성 문제를 해결하기 위해 균형잡힌 데이터 증강을 적용하여 학습 데이터를 확대하였다. DLN 모델은 대다수의 교량이 D등급에 도달할 것으로 예측한 반면, XGBoost는 예측값 포화로 인해 극히 일부만 도달할 것으로 예측하였다. 데이터 증강은 예측 오차를 크게 감소시키고 희소 고결함도 구간의 테스트 샘플 수를 대폭 증가시켜 예측 성능을 현저히 개선하였다. 본 연구는 단조성 제약과 균형잡힌 데이터 증강의 결합이 교량 열화 예측에서 외삽 문제와 불균형 데이터 문제를 효과적으로 해결하여 현실적인 장기 유지관리 계획 수립의 가능성을 제시하였다.
-
Data Augmentation and Interpretable Deep Learning for Remaining Life Prediction of Highway Bridges
-
Technical Note
-
Design and Construction of Pocheon Y-Shaped Suspension Bridge
포천 Y형 출렁다리의 설계 및 시공
-
Sang Hun Shin, Ho-Kyung Kim, Dae Young Lee, Jeong Kyoon An
신상훈, 김호경, 이대영, 안정균
- The Pocheon Hantan River Y-Shaped Suspension Bridge, installed in Pocheon-si Gyeonggi-do is an asymmetric Y-shape bridge, designed to improve tourist convenience and …
경기도 포천시에 설치된 포천 Y형 출렁다리는 비대칭 Y자형 구조로, 관광객들의 편의를 증진하기 위해 설계되었다. 비대칭 교량의 구조적 안정성을 확보하기 위해서 중앙부의 이중 …
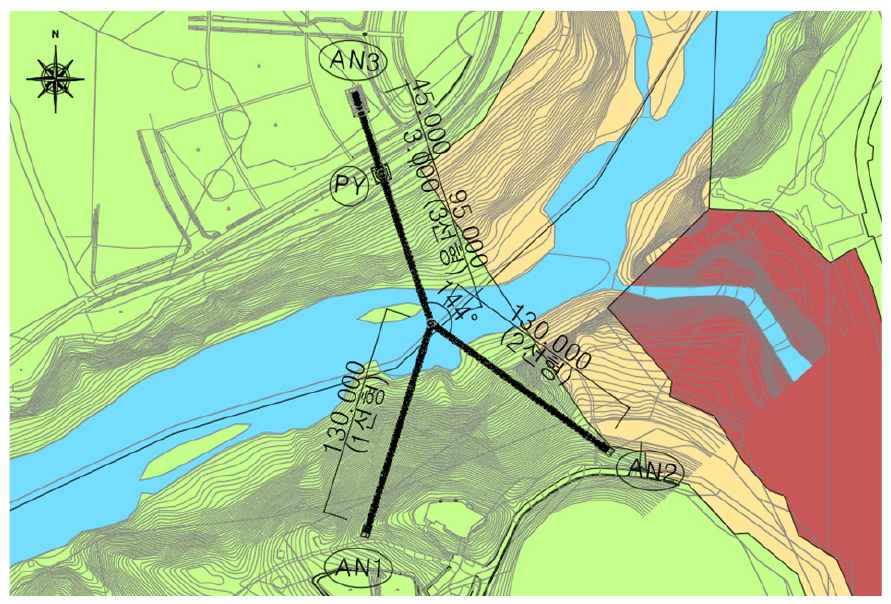
- The Pocheon Hantan River Y-Shaped Suspension Bridge, installed in Pocheon-si Gyeonggi-do is an asymmetric Y-shape bridge, designed to improve tourist convenience and also to form a tourism chain by connecting existing trails. To ensure the structural integrity and meticulous construction management of the bridge, innovative techniques such as the central duplex structure, continuous cabling at the central part, and shape control using Global Navigation Satellite System were employed.
- COLLAPSE
경기도 포천시에 설치된 포천 Y형 출렁다리는 비대칭 Y자형 구조로, 관광객들의 편의를 증진하기 위해 설계되었다. 비대칭 교량의 구조적 안정성을 확보하기 위해서 중앙부의 이중 구조 및 중앙부에서의 연속적인 케이블 구조가 적용되었으며 정밀 구조검토를 통하여 주요 부재들의 안정성을 확인하였다. 또한 정밀한 시공 관리를 보장하기 위해 글로벌 위성항법시스템(GNSS) 및 AIoT센서 등 혁신적인 기술이 적용되었다.
-
Design and Construction of Pocheon Y-Shaped Suspension Bridge
-
Research Article
-
Comparative study for enhancing PCA-Based Anomaly Detection with Missing Values
결측치 처리에 따른 PCA 기반 구조물 이상상태 탐지 신뢰성 향상 연구
-
Jaeseok Jung, Seung-Seop Jin
정재석, 진승섭
- Vibration-based Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) provides modal information, such as natural frequencies, which is essential for structural state diagnosis. However, depending on …
진동 기반 구조물 건전성 모니터링(SHM)은 구조물 상태 진단에 필요한 모드 정보(고유진동수 등)를 통해 제공한다. 하지만 가진 조건 등 외부 조건에 따라 일부 …
- Vibration-based Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) provides modal information, such as natural frequencies, which is essential for structural state diagnosis. However, depending on external factors like excitation conditions, certain modes are frequently missing over time. These frequent missing values are a primary factor that degrades anomaly detection performance. In this study, a fundamental investigation was conducted to enhance the reliability of Principal Component Analysis (PCA)-based structural anomaly detection in realistic environments containing missing values. To achieve this, we compared imputation-based approaches (KNN, MICE), which fill in missing values prior to PCA, with a method that intrinsically handles missing values within the PCA algorithm itself. Numerical experiments considering various missing rates and patterns were conducted to evaluate the performance of these methodologies, and based on the results, directions for future research are proposed.
- COLLAPSE
진동 기반 구조물 건전성 모니터링(SHM)은 구조물 상태 진단에 필요한 모드 정보(고유진동수 등)를 통해 제공한다. 하지만 가진 조건 등 외부 조건에 따라 일부 모드들이 시간에 따라 누락되어 결측되는 문제가 존재한다. 이러한 잦은 결측치는 탐지 성능을 저해하는 주요 원인 중 하나이다. 본 연구에서는 결측치가 발생하는 실제 환경에서도 주성분 분석(PCA) 기반 구조물 이상상태 탐지의 신뢰성을 향상시키는 기초 연구를 수행하였다. 이를 위해 PCA 적용 전 결측치를 보간하는 방법(KNN, MICE)과 PCA 알고리즘 자체 내에서 결측치를 처리할 수 있는 방법을 비교하였다. 다양한 결측률 및 결측치 유형에 대한 수치 실험을 상기 방법론들의 성능을 평가하였으며, 그 결과를 토대로 향후 연구 방향을 제시하였다.
-
Comparative study for enhancing PCA-Based Anomaly Detection with Missing Values
-
Technical Note

-
Proposal of a Hyperboloid Cable-Net Structure and its Application to the Design and Construction of a Suspension Footbridge
하이퍼볼로이드 케이블-네트 구조 제안 및 현수 보도교의 설계 및 시공
-
Jin Woo Jeong, Jin Lee, Seung Hye Lee
정진우, 이진, 이승혜
- The Hantangang canyon, a UNESCO Global Geopark, presents significant geotechnical challenges for bridge construction. This paper introduces the design and construction of …
유네스코(UNESCO) 세계지질공원인 한탄강 협곡은 독특한 주상절리 지형으로 인해 교량 건설에 큰 제약이 따른다. 본 연구는 이러한 환경적 제약을 극복하기 위해 설계 및 …
- The Hantangang canyon, a UNESCO Global Geopark, presents significant geotechnical challenges for bridge construction. This paper introduces the design and construction of the ‘Durumi Footbridge’, a 201 m hyperboloid cable-net suspension footbridge. The proposed system leverages its 3D geometric configuration integrated with internal cable tension to achieve geometric stiffness, ensuring superior aeroelastic stability without additional wind cables. Furthermore, this study details the specialized ‘feeding method’ for ring beam installation and precise shape control. This case study offers an innovative engineering solution for long-span bridges in sensitive natural environments.
- COLLAPSE
유네스코(UNESCO) 세계지질공원인 한탄강 협곡은 독특한 주상절리 지형으로 인해 교량 건설에 큰 제약이 따른다. 본 연구는 이러한 환경적 제약을 극복하기 위해 설계 및 시공된 연장 201 m의 하이퍼볼로이드 케이블-네트 보도교인 ‘두루미 보도교’ 사례를 고찰한다. 제안된 구조는 입체적인 기하학적 형상과 내부 장력의 상호작용을 통해 기하강성을 확보하며, 별도의 외부 내풍 케이블 없이도 우수한 공탄성 안정성을 제공한다. 또한 원형 링 빔 가설을 위한 ‘피딩 공법(feeding method)’과 단계별 형상 관리 과정을 상세히 기술한다. 본 사례는 지형적 난조건을 가진 장경간 보도교 설계 및 시공의 실무적 대안을 제시한다.
-
Proposal of a Hyperboloid Cable-Net Structure and its Application to the Design and Construction of a Suspension Footbridge
-
Research Article
-
Analysis of Extreme Metocean Condition Variations with Observation Period for IFORM-Based Offshore Wind Design
관측기간에 따른 극한 해양환경 조건의 변화 분석: IFORM 기반 해상풍력 설계 해양조건 산정
-
Kyungrok Kwon, Jong Gyun Paik, Jin Man Mok, Jung-Sik Kong
권경록, 백종균, 목진만, 공정식
- For offshore wind turbine design, reliable observations of significant wave height and wind speed are essential, and thus metocean buoy data that …
해상풍력 터빈 설계를 위해서는 유의파고와 풍속에 대한 신뢰성 있는 관측이 필수적이며, 이를 위해 두 변수를 동시에 계측하는 해양 기상 부이 자료가 필요하다. …
- For offshore wind turbine design, reliable observations of significant wave height and wind speed are essential, and thus metocean buoy data that simultaneously measure these variables are required. However, most metocean buoys have relatively short observation periods, which limits the reliability of estimating extreme metocean conditions. In this study, an environmental contour–based joint distribution approach is adopted to compare and analyze the differences in extreme metocean conditions depending on the observation period.
- COLLAPSE
해상풍력 터빈 설계를 위해서는 유의파고와 풍속에 대한 신뢰성 있는 관측이 필수적이며, 이를 위해 두 변수를 동시에 계측하는 해양 기상 부이 자료가 필요하다. 그러나 대부분의 해양 기상 부이는 관측기간이 상대적으로 짧아 극한 해양환경 조건을 신뢰성 있게 추정하는 데 한계가 있다. 본 연구에서는 환경등고선에 기반한 결합분포 접근법을 적용하여, 관측기간에 따라 극한 해양환경 조건의 변화를 비교·분석하였다.
-
Analysis of Extreme Metocean Condition Variations with Observation Period for IFORM-Based Offshore Wind Design
-
Technical Note
-
Analysis of Long-Term Structural Behavior of a Three-Dimensional Self-Anchored Suspension Bridge
3차원 자정식 현수교의 장기 구조거동 특성 분석
-
In Hwan Bae
배인환
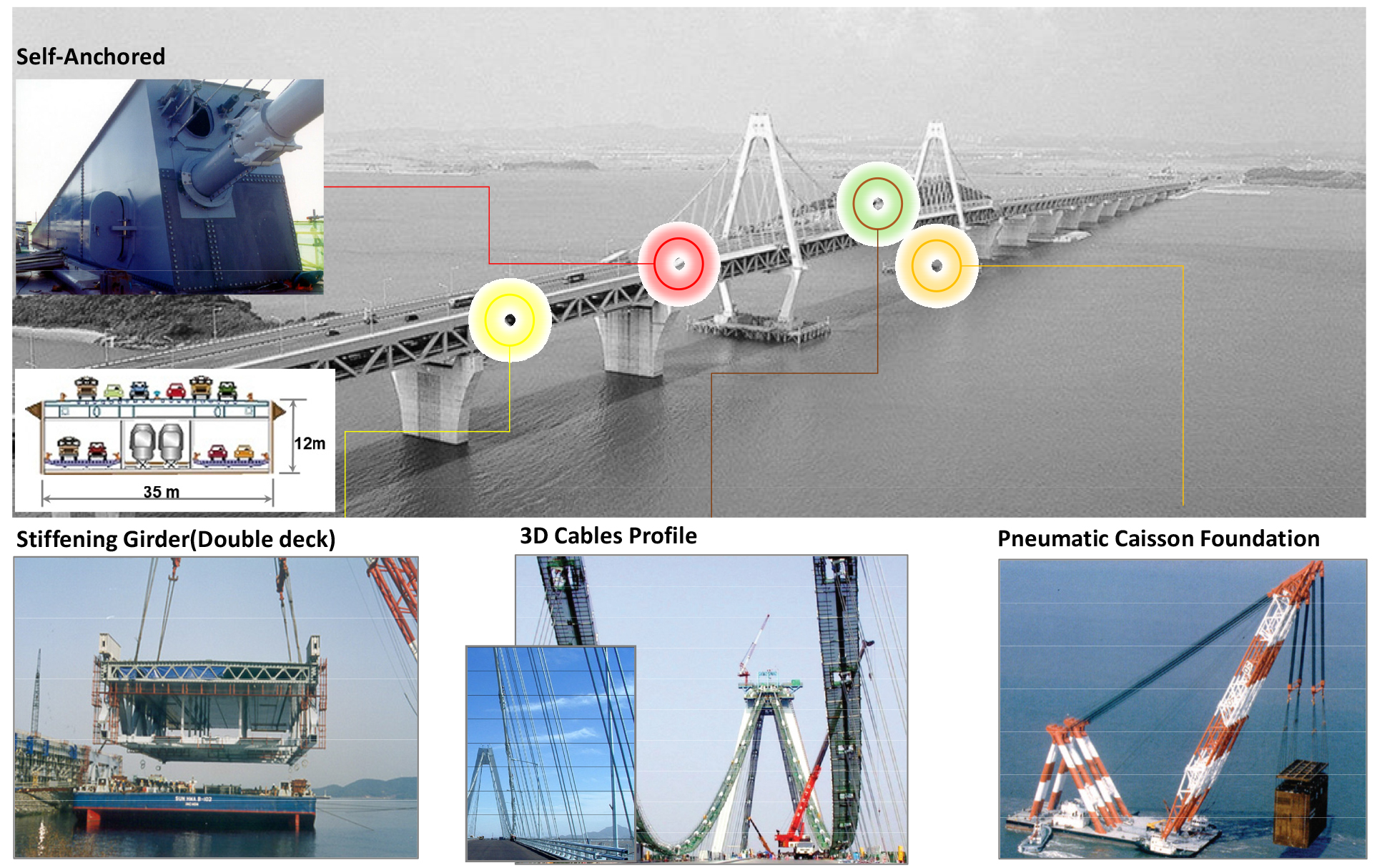
- The Yeongjong bridge is a three-dimensional self-anchored suspension bridge that carries both roadway and railway traffic, characterized by its unique structural features. …
영종대교 현수교는 도로와 철도 병용의 3차원 자정식 현수교로서 일반교량과는 다른 독특한 구조적 특성을 가지고 있으며, 설계기법의 유효성 검증, 환경 및 하중영향 검토, …
- The Yeongjong bridge is a three-dimensional self-anchored suspension bridge that carries both roadway and railway traffic, characterized by its unique structural features. A structural health monitoring system (SHMS) has been developed and installed to verify the effectiveness of the design and to evaluate the structural safety of the bridge. The roadway began operation in December 2000 and railway facilities were installed in 2004, resulting in an increase in dead load. The KTX train operated on the bridge for four years starting in 2014. This study analyzes the long-term time-dependent behavior of the bridge based on SHMS data. Variations in hanger tension forces, decreases in cable-band bolt axial forces, and changes in long-term deformation characteristics during service were analyzed. In addition, the dynamic characteristics of the suspension bridge were analyzed to establish a structural health index (HI) and the corresponding evaluation criteria. The findings indicate that the bridge has maintained satisfactory structural integrity throughout its service.
- COLLAPSE
영종대교 현수교는 도로와 철도 병용의 3차원 자정식 현수교로서 일반교량과는 다른 독특한 구조적 특성을 가지고 있으며, 설계기법의 유효성 검증, 환경 및 하중영향 검토, 구조안전 및 재난관리를 위하여 구조건전도모니터링 시스템(Bridge Health Monitoring System, SHMS)이 구축되어 운영되고 있다. 영종대교는 2000년 12월에 도로부가 준공되었고, 공용중 2004년에 철도레일 설치로 사하중이 증가하였고, 2014년 KTX운행 등 사용환경의 변화를 겪었다. 장기간 계측결과를 근거로 공용중 사용환경 변화에 따른 행어장력특성, 밴드볼트 축력 저하 특성, 장기 형상거동변화특성 등을 규명하였다. 또한 현수교의 동특성 분석을 통하여 구조건전도지수와 평가기준을 수립하였고 평가결과, 구조건전성을 확보하고 있는 것을 확인하였다.
-
Analysis of Long-Term Structural Behavior of a Three-Dimensional Self-Anchored Suspension Bridge
-
Research Article
-
Rapid Wildfire Spread Prediction Model Based on Probabilistic Conditional GAN
확률론적 조건부 GAN 기반 신속 산불 확산 예측 모델
-
Taehoon Kang, Taeyong Kim
강태훈, 김태용
- To address the increasing scale of wildfires due to recent climate change, this study proposes a rapid and probabilistic wildfire spread prediction …
최근 기후변화로 인한 산불의 대형화에 대응하기 위해, 본 연구는 조건부 생성적 적대 신경망을 활용한 신속하고 확률론적인 산불 확산 예측 모델을 제안한다. 제안된 …
- To address the increasing scale of wildfires due to recent climate change, this study proposes a rapid and probabilistic wildfire spread prediction model using a conditional Generative Adversarial Network. The proposed model is trained on a large-scale dataset constructed via FARSITE simulations, securing both the precision of physics-based models and the computational speed of deep learning. Experimental results demonstrate that the model addresses the ambiguity of spread boundaries and under-estimation issues found in existing Autoencoder-based models by generating sharp fire shapes, while achieving a breakthrough in prediction speed compared to physics-based simulations. Furthermore, by introducing an ensemble technique to quantify uncertainty and providing various spread scenarios, it is confirmed that the model can effectively support the decision-making of field commanders. This study suggests that generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology can be utilized as a key component of real-time wildfire disaster prevention systems.
- COLLAPSE
최근 기후변화로 인한 산불의 대형화에 대응하기 위해, 본 연구는 조건부 생성적 적대 신경망을 활용한 신속하고 확률론적인 산불 확산 예측 모델을 제안한다. 제안된 모델은 FARSITE 시뮬레이션을 통해 구축된 대규모 데이터셋을 학습하여 물리 기반 모델의 정밀함과 딥러닝의 연산 속도를 동시에 확보하였다. 실험 결과 본 모델은 기존 오토인코더 기반 모델에서 나타나는 확산 경계의 모호성 및 과소예측 문제를 극복하고 선명한 화재 형상을 생성하였으며 물리 기반 시뮬레이션 대비 획기적인 예측 속도를 달성하였다. 또한 앙상블 기법을 도입하여 불확실성을 정량화하고 다양한 확산 시나리오를 제공함으로써 현장 지휘관의 의사결정을 효과적으로 지원할 수 있음을 확인하였다. 본 연구는 생성형 AI 기술이 실시간 산불 방재 시스템의 핵심 요소로 활용될 수 있음을 시사한다.
-
Rapid Wildfire Spread Prediction Model Based on Probabilistic Conditional GAN
-
Technical Note
-
Design of the Circular Walkway near Ngong Ping Village in Hong Kong
홍콩 옹핑 마을 인근 원형 산책로의 계획과 설계
-
Geon Woo Song, Jeong Won An, Joon Hyung Lee, Jun Soo Kim
송건우, 안정원, 이준형, 김준수
- This paper proposes a conceptual design for a circular elevated walkway in Ngong Ping Village, emphasizing harmony between the mountainous landscape and …
본 논문은 홍콩 응옹핑 마을(Ngong Ping Village)을 대상으로, 산악 지형 및 불교적 상징성과의 조화를 고려한 원형 고가 산책로의 개념 설계를 제안한다. 제안된 …
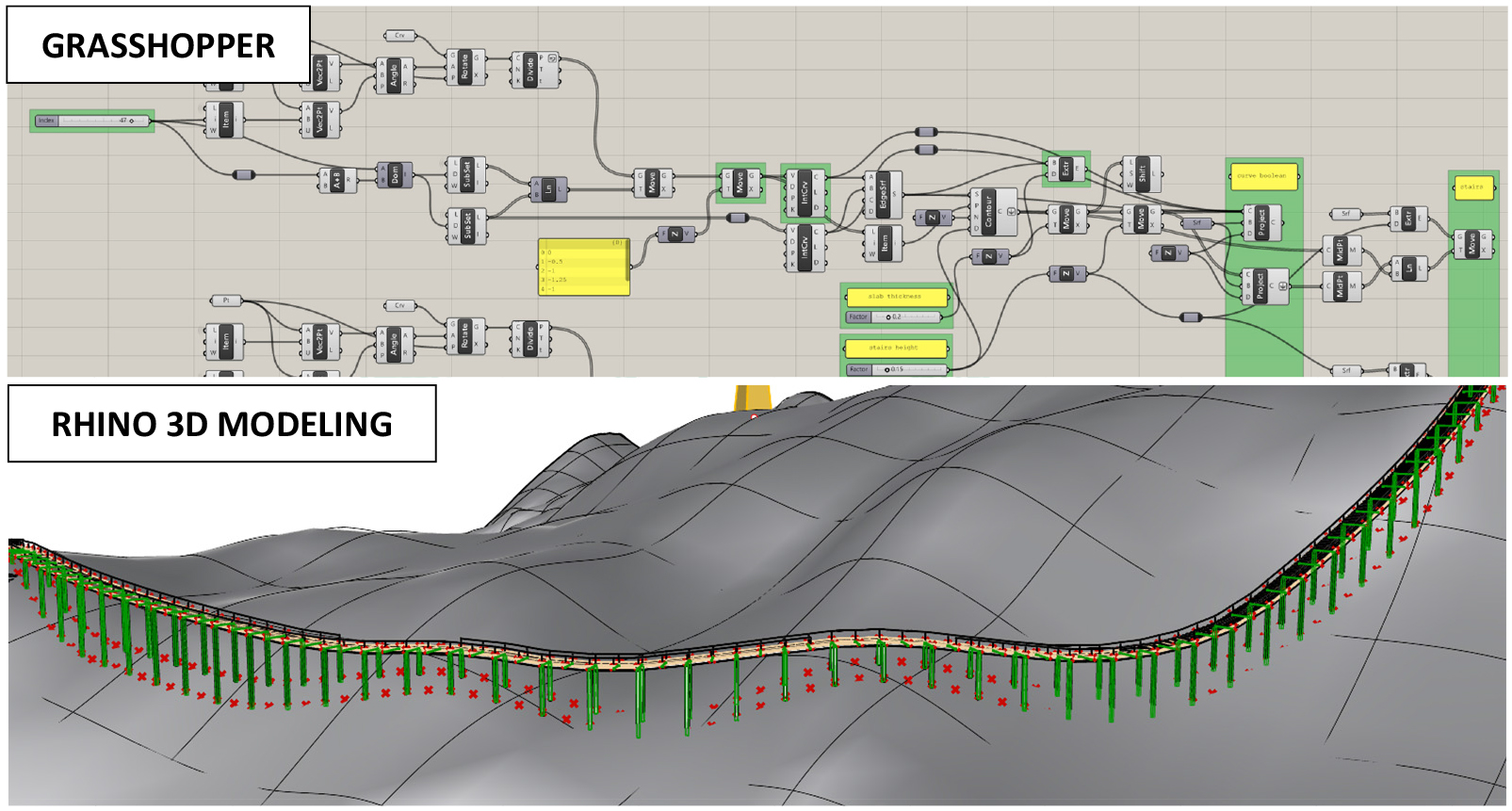
- This paper proposes a conceptual design for a circular elevated walkway in Ngong Ping Village, emphasizing harmony between the mountainous landscape and the site’s Buddhist symbolism. The walkway adopts a circular geometry to represent the Buddhist cycle of life and to provide a continuous spatial journey. A spreadsheet-based process was used to optimize the walkway slope for pedestrian comfort, while Grasshopper enabled a parametric 3D modelling system for rapid and flexible design updates. In addition, the curved bridge segment of the walkway, supported by a spatial arch, was structurally analyzed using MIDAS Civil to verify feasibility.
- COLLAPSE
본 논문은 홍콩 응옹핑 마을(Ngong Ping Village)을 대상으로, 산악 지형 및 불교적 상징성과의 조화를 고려한 원형 고가 산책로의 개념 설계를 제안한다. 제안된 산책로는 불교의 윤회 사상을 상징하는 원형 기하를 채택하여, 이용자에게 연속적인 공간적 경험을 제공하도록 계획되었다. 보행자의 이용 편의성을 확보하기 위하여 스프레드시트 기반의 경사 최적화 과정을 통해 산책로의 종단 기울기를 조정하였으며, Grasshopper를 활용한 파라메트릭 3차원 모델링 시스템을 구축하여 설계 변수 변화에 따른 형상을 신속하고 유연하게 반영할 수 있도록 하였다. 또한 산책로의 일부 구간에 적용된 공간 아치(spatial arch) 지지 곡선 교량에 대해서는 MIDAS Civil을 이용한 구조해석을 수행하여 구조적 적용 가능성을 검토하였다.
-
Design of the Circular Walkway near Ngong Ping Village in Hong Kong
-
Research Article
-
CTGAN-Based Data Sampling for Prediction of Bridge Safety Rating
교량 안전등급 예측을 위한 CTGAN 기반 데이터 샘플링
-
Jisu Hong, Se-Jin Jeon
홍지수, 전세진
- Dataset related to safety rating of bridges often suffers from limited reliability and severe class imbalance, which hinders the development of AI(Artificial …
국내 교량 안전등급 데이터는 신뢰성의 한계와 등급 분포의 불균형 문제로 인해 인공지능 기반 예측 모델의 성능 확보에 어려움이 존재한다. 이 연구에서는 이러한 …
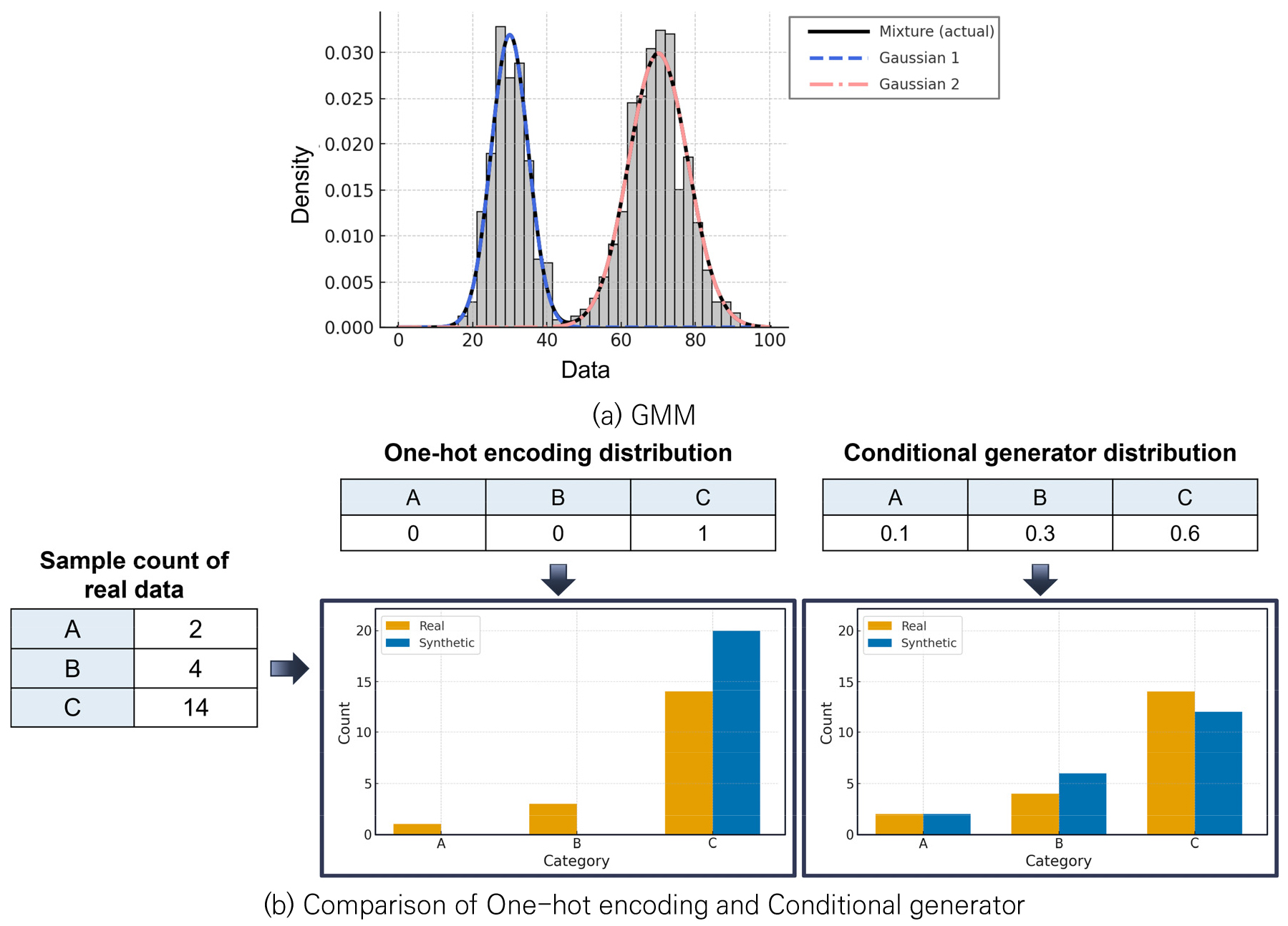
- Dataset related to safety rating of bridges often suffers from limited reliability and severe class imbalance, which hinders the development of AI(Artificial Intelligence) models. To address these challenges, this study implemented a comprehensive data preprocessing focused on improving data quality and incorporating key factors related to safety rating of bridges. Inspection reliability was enhanced by integrating detailed results from in-depth and precise safety inspections, and additional variables representing maintenance history and environmental conditions were introduced to better capture factors affecting safety performance. Because the dataset exhibits a highly imbalanced class distribution, which is difficult to resolve using traditional sampling techniques, this study adopted the Conditional Tabular Generative Adversarial Network(CTGAN), a generative model specialized for tabular data. CTGAN was used to synthesize minority-class samples while preserving the original distribution of the majority class, enabling balanced learning without data loss. Overall, the results demonstrate that CTGAN-based data sampling offers an effective alternative for handling imbalanced dataset that contains both categorical and numerical variables, such as bridge safety ratings. The proposed approach is expected to contribute to improving the performance of future AI-based models for bridge safety assessment and related decision-making in infrastructure maintenance.
- COLLAPSE
국내 교량 안전등급 데이터는 신뢰성의 한계와 등급 분포의 불균형 문제로 인해 인공지능 기반 예측 모델의 성능 확보에 어려움이 존재한다. 이 연구에서는 이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해 데이터 신뢰성 향상과 안전등급 관련 주요 인자의 확보에 중점을 둔 전처리 절차를 수행하고, 표 형식의 데이터 생성이 가능한 Conditional Tabular Generative Adversarial Networks(CTGAN) 기반 합성 데이터 기법을 도입하였다. 정밀안전점검 및 진단 결과를 반영하도록 하여 안전등급 결과를 개선하고, 유지관리 이력 및 환경 특성을 고려한 변수를 추가하여 교량 안전등급 데이터를 구축하였다. 교량의 안전등급 데이터의 경우 전통적 샘플링 기법을 통해 불균형 분포를 해결하기 어렵기 때문에, CTGAN 기반 합성 데이터 기법을 적용하여 소수 클래스의 분포를 실제 데이터와 유사한 형태로 재현하고, 다수 클래스의 본래 분포를 유지하여 데이터의 손실 없이 학습 데이터의 균형을 확보하였다. 따라서, 이 연구는 CTGAN 기반 샘플링이 교량 안전등급과 같이 범주형 및 수치형 변수가 혼재되고 불균형 분포인 데이터에서 효과적인 대안이 될 수 있음을 제시하였으며, 향후 교량 안전등급 예측과 같은 유지관리 의사결정 모델의 성능 향상에 기여할 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
CTGAN-Based Data Sampling for Prediction of Bridge Safety Rating
-
Research Article
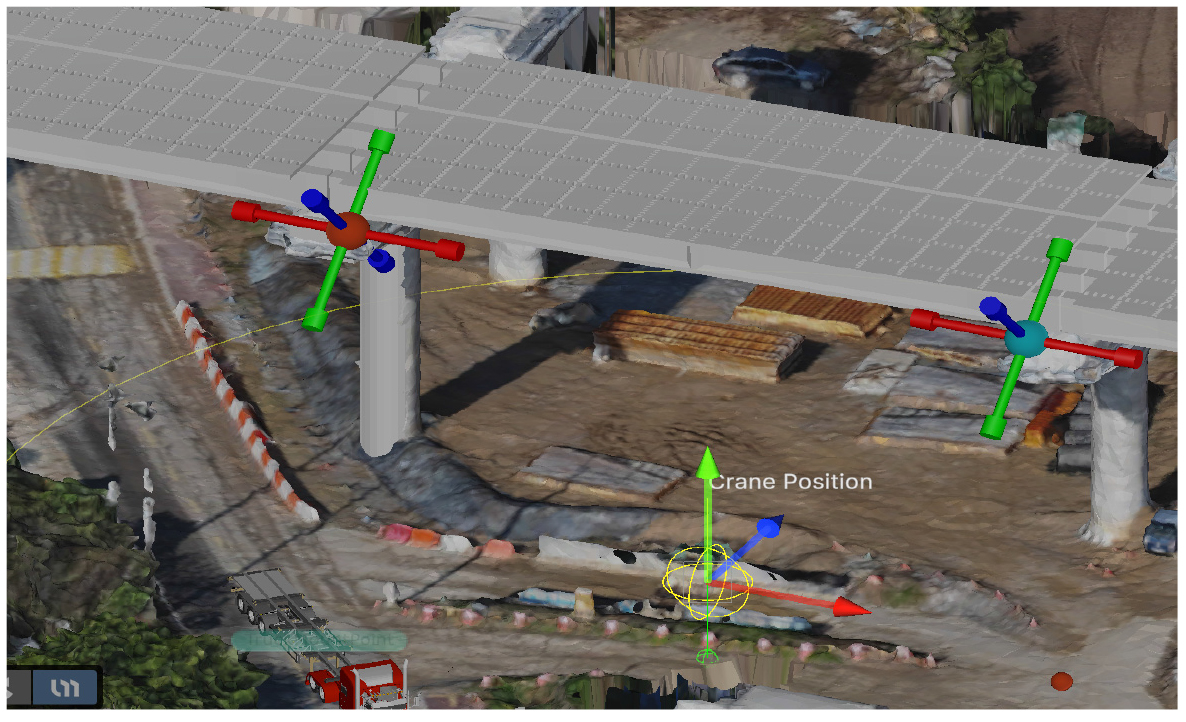
-
Development of a Crane Operation Location Optimization System for Prefabricated Bridge Deck Installation Using Relative Coordinate-Based Automatic Search Algorithm
상대좌표계 기반 자동 탐색 알고리즘을 활용한 프리팹 교량 바닥판 설치용 크레인 작업위치 최적화 시스템 개발
-
Dae Ho Jang, Chang Su Shim
장대호, 심창수
- This study presents the development of a Construction Digital Twin (CDT) system designed to optimize crane operations during the installation of prefabricated …
이 연구는 조립식 교량 바닥판 설치 시 크레인 운영을 최적화하기 위해 설계된 건설 디지털 트윈(CDT) 시스템의 개발을 제시한다. 제안된 시스템은 이전의 CDT …
- This study presents the development of a Construction Digital Twin (CDT) system designed to optimize crane operations during the installation of prefabricated bridge decks. Building upon the previous CDT framework, the proposed system introduces a relative coordinate system and an automatic search algorithm to overcome the complexity and surveying dependency inherent in conventional absolute coordinate-based methods. The relative coordinate system defines spatial relationships directly with reference to on-site structures, enabling intuitive and efficient setup of construction environments. Implemented using the Unity engine, the CDT system integrates a grid-based optimization module that automatically identifies the optimal crane positions and simulates lifting operations in real time to verify work feasibility and safety. Field applications confirmed that the system significantly reduces crane repositioning frequency and overall operation time, demonstrating its effectiveness in enhancing construction efficiency. The research contributes a practical and scalable digital twin solution that supports data-driven decision-making and can be readily deployed in actual construction sites without additional surveying processes.
- COLLAPSE
이 연구는 조립식 교량 바닥판 설치 시 크레인 운영을 최적화하기 위해 설계된 건설 디지털 트윈(CDT) 시스템의 개발을 제시한다. 제안된 시스템은 이전의 CDT 프레임워크를 기반으로 하여 기존의 절대 좌표계 기반 방법에 내재된 복잡성과 측량 의존성을 극복하기 위해 상대 좌표계와 자동 탐색 알고리즘을 도입하였다. 상대 좌표계는 현장 구조물을 참조하여 공간 관계를 직접 정의하여 직관적이고 효율적인 건설 환경 설정을 가능하게 한다. Unity 엔진을 사용하여 구현된 CDT 시스템은 그리드 기반 최적화 모듈을 통합하여 최적의 크레인 위치를 자동으로 식별하고 실시간으로 인양 작업을 시뮬레이션하여 작업 타당성과 안전성을 검증하였다. 현장 적용 결과, 시스템이 크레인 재배치 빈도와 전체 작업 시간을 크게 줄여 건설 효율성을 향상시키는 데 효과적임을 확인하였다. 이 연구는 데이터 기반 의사결정을 지원하고 추가 측량 과정 없이 실제 건설 현장에 쉽게 배포할 수 있는 실용적이고 확장 가능한 디지털 트윈 솔루션에 기여하였다.
-
Development of a Crane Operation Location Optimization System for Prefabricated Bridge Deck Installation Using Relative Coordinate-Based Automatic Search Algorithm
-
Research Article
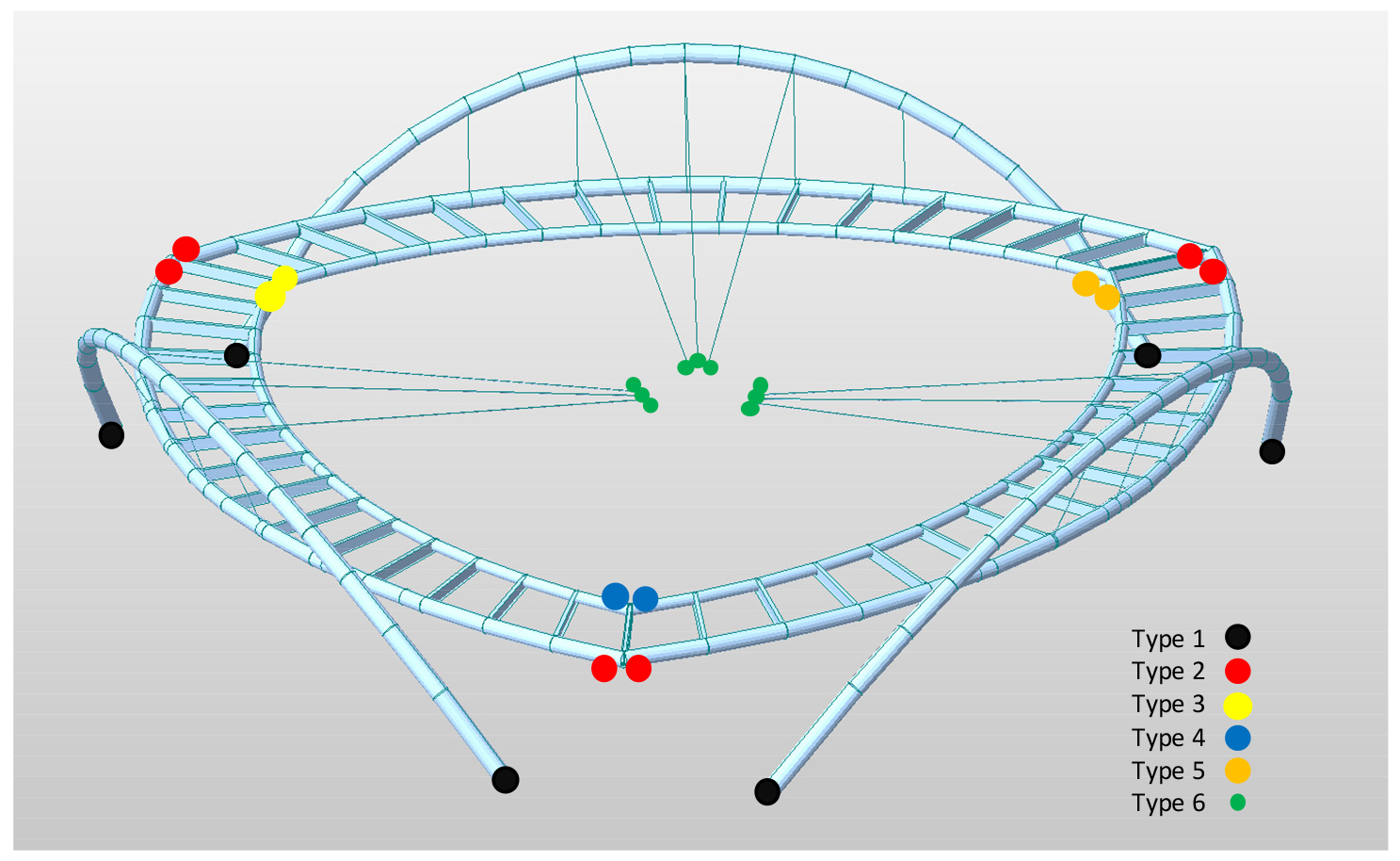
-
Concept Design Development of Three-Span Curved Arch Pedestrian Bridge Tied by Cable-Ring Structure
케이블-링 구조로 결속된 3경간 곡선 아치 보행교의 개념 설계 개발
-
MinHo Yu, Hyoju Oh, Wonsuk Park
유민호, 오효주, 박원석
- This paper presents the conceptual design process of a ring-shaped pedestrian bridge proposed for the Shibuya Scramble Crossing, developed for the IABSE …
이 논문은 2025년 IABSE Young Engineers Colloquium East Asia and Germany in Tokyo에서 제안된 시부야 스크램블 교차로 상부 환형 보행교의 개념 설계 …
- This paper presents the conceptual design process of a ring-shaped pedestrian bridge proposed for the Shibuya Scramble Crossing, developed for the IABSE Young Engineers Colloquium East Asia and Germany in Tokyo 2025. The objective is to demonstrate how abstract urban concepts and site-specific constraints can be transformed into a structurally feasible bridge system using undergraduate-level structural engineering knowledge. Based on the symbolic concept of Moyai - meaning “to unite”- the bridge was conceived as a curved triangular ring integrating urban space, nature, and human activity. Structurally, the bridge consists of three curved girder spans supported by inclined arches and hangers, with the arches mutually restrained by a central ring-cable system to resist overturning. A three-dimensional frame model was developed in MIDAS Civil, and an iterative linear analysis procedure was used to estimate the initial equilibrium state of the cable-arch system under self-weight. The results confirm the structural feasibility of the proposed form and its suitability as an educational case study for conceptual bridge design.
- COLLAPSE
이 논문은 2025년 IABSE Young Engineers Colloquium East Asia and Germany in Tokyo에서 제안된 시부야 스크램블 교차로 상부 환형 보행교의 개념 설계 과정을 제시한다. 본 연구의 목적은 도시 맥락과 추상적 개념을 학부 수준의 구조공학 지식을 활용하여 구조적으로 구현 가능한 교량 형식으로 발전시키는 방법을 보여주는 데 있다. “함께 묶다”라는 의미를 가진 Moyai 개념을 바탕으로, 도시・자연・인간의 조화를 곡선 삼각형 링 형상으로 표현하였다. 제안된 교량은 경사 아치와 행어 케이블로 지지되는 3경간 곡선 거더와, 중앙 링-케이블 시스템에 의해 상호 결속되어 전도에 저항하는 구조 형식을 갖는다. MIDAS Civil을 이용한 3차원 뼈대 해석과 반복적 선형해석을 통해 케이블-아치 시스템의 초기 평형 상태를 추정하였으며, 이를 통해 제안 형상의 구조적 실현 가능성과 교육적 활용성을 확인하였다.
-
Concept Design Development of Three-Span Curved Arch Pedestrian Bridge Tied by Cable-Ring Structure
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of Structure Research and Practice
Journal of Structure Research and Practice
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of Structure Research and Practice
Journal of Structure Research and Practice










